Squid is a full-featured Linux-based proxy application mostly used for filtering traffic, security, and DNS lookups. It is also used to improve the web server performance by caching resources. In simple terms, a Squid server is a computer that acts as an intermediary between a desktop computer and the internet that redirects inbound client requests to a server where data is stored for easier retrieval. It supports several protocols including, HTTP, FTP, TLS, SSL, Internet Gopher and HTTPS.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install and set up Squid proxy server on Ubuntu 20.04 server.
Prerequisites
- A server running Ubuntu 20.04.
- A root password is configured the server.
Getting Started
Before starting, you will need to update your system packages to the latest version. You can update them with the following command:
apt-get update -yOnce all the packages are updated, restart your system to apply the changes.
Install Squid Proxy
By default, the Squid package is available in the Ubuntu 20.04 default repository. You can install it using the following command:
apt-get install squid -yOnce the Squid is installed, you can check the status of the Squid service with the following command:
systemctl status squidYou should get the following output:
? squid.service - Squid Web Proxy Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/squid.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2020-08-23 12:00:24 UTC; 11s ago
Docs: man:squid(8)
Process: 49265 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/squid --foreground -z (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 49282 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/squid -sYC (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 49283 (squid)
Tasks: 4 (limit: 2353)
Memory: 16.4M
CGroup: /system.slice/squid.service
??49283 /usr/sbin/squid -sYC
??49285 (squid-1) --kid squid-1 -sYC
??49287 (logfile-daemon) /var/log/squid/access.log
??49288 (pinger)
Aug 23 12:00:24 ubuntu2004 squid[49285]: Max Swap size: 0 KB
Aug 23 12:00:24 ubuntu2004 squid[49285]: Using Least Load store dir selection
Aug 23 12:00:24 ubuntu2004 squid[49285]: Set Current Directory to /var/spool/squid
Aug 23 12:00:24 ubuntu2004 squid[49285]: Finished loading MIME types and icons.
Aug 23 12:00:24 ubuntu2004 squid[49285]: HTCP Disabled.
Aug 23 12:00:24 ubuntu2004 squid[49285]: Pinger socket opened on FD 14
Aug 23 12:00:24 ubuntu2004 squid[49285]: Squid plugin modules loaded: 0
Aug 23 12:00:24 ubuntu2004 squid[49285]: Adaptation support is off.
Aug 23 12:00:24 ubuntu2004 squid[49285]: Accepting HTTP Socket connections at local=[::]:3128 remote=[::] FD 12 flags=9
Aug 23 12:00:25 ubuntu2004 squid[49285]: storeLateRelease: released 0 objects
By default, Squid is listening on port 3128. You can check it with the following command:
netstat -plunt | grep 3128You should see the following output:
tcp6 0 0 :::3128 :::* LISTEN 50017/(squid-1)
Once you are finished, you can prceed to the next step.
Set Up IP Based Authentication
There are several ways you can restrict the client to access the internet. In this section, we will set up Squid to authenticate based on Client’s IP address.
You can do it by editing Squid default configuration file:
nano /etc/squid/squid.confAdd the following line at the beginning of the file:
acl client1 src 192.168.10.10 acl client2 src 192.168.10.11 http_access allow client1 client2
Save and close the file when you are finished. Then restart the Squid service to apply the changes:
systemctl restart squidWhere:
- client1 and client2 is the name that identified the client computers.
- 192.168.10.10 and 192.168.10.11 is the IP address of the client computer.
Now, only computers that are configured with IP 192.168.10.10 and 192.168.10.11 can access the internet.
Set Up User Based Authentication
You can also set up Squid to authenticate based on user and password. To do so, you will need to install Apache utils package in your system.
Run the following command to install the Apache utils package:
apt install apache2-utils -yOnce installed, create a first user with the following command:
htpasswd /etc/squid/passwd client1You will be asked to set a password as shown below:
New password: Re-type new password: Adding password for user client1
Next, create a second user with the following command:
htpasswd /etc/squid/passwd client2Set your password as shown below:
New password: Re-type new password: Adding password for user client2
Next, you can verify both users using the following command:
cat /etc/squid/passwdYou should get the following output:
client1:$apr1$CPlx8eVt$NJq3CT/hzfDCnAZRypIq5/ client2:$apr1$XYxQ2npc$IW0Nqjp15O5WYCo/wCFlB0
Next, open the Squid default configuration file:
nano /etc/squid/squid.confRemove the first three lines which you have added in previous section and add the following lines at the beginning of the file:
auth_param basic program /usr/lib/squid3/basic_ncsa_auth /etc/squid/passwd acl ncsa_users proxy_auth REQUIRED http_access allow ncsa_users
Save and close the file. Then, restart the Squid proxy service to apply the changes:
systemctl restart squidNow, you will need to provide username and password in order to access the internet.
Set Up Combined Authentication
You can also set up a Squid to authenticate a client based on the IP address and username / password.
Open the Squid default configuration file:
nano /etc/squid/squid.confFind the following lines which you have added in previous section:
auth_param basic program /usr/lib/squid3/basic_ncsa_auth /etc/squid/passwd acl ncsa_users proxy_auth REQUIRED http_access allow ncsa_users
And, replace them with the following lines:
acl client1 src 192.168.10.10 acl client2 src 192.168.10.11 auth_param basic program /usr/lib/squid3/basic_ncsa_auth /etc/squid/passwd acl ncsa_users proxy_auth REQUIRED http_access allow client1 client2 ncsa_users
Save and close the file when you are finished then restart the Squid service to apply the changes:
systemctl restart squidSet Up Squid to Anonymize Traffic
Next, you will need to add some rules to mask client IP addresses from the servers that receive traffic from your Squid HTTP proxy.
You can do it by editing the Squid default configuration file:
nano /etc/squid/squid.confAdd the following lines at the beginning of the file:
forwarded_for off request_header_access Allow allow all request_header_access Authorization allow all request_header_access WWW-Authenticate allow all request_header_access Proxy-Authorization allow all request_header_access Proxy-Authenticate allow all request_header_access Cache-Control allow all request_header_access Content-Encoding allow all request_header_access Content-Length allow all request_header_access Content-Type allow all request_header_access Date allow all request_header_access Expires allow all request_header_access Host allow all request_header_access If-Modified-Since allow all request_header_access Last-Modified allow all request_header_access Location allow all request_header_access Pragma allow all request_header_access Accept allow all request_header_access Accept-Charset allow all request_header_access Accept-Encoding allow all request_header_access Accept-Language allow all request_header_access Content-Language allow all request_header_access Mime-Version allow all request_header_access Retry-After allow all request_header_access Title allow all request_header_access Connection allow all request_header_access Proxy-Connection allow all request_header_access User-Agent allow all request_header_access Cookie allow all request_header_access All deny all
Save and close the file when you are finished then restart the Squid service to apply the changes:
systemctl restart squidVerify Squid Proxy
Next, you will need to define your Proxy server in your Mozilla web browser.
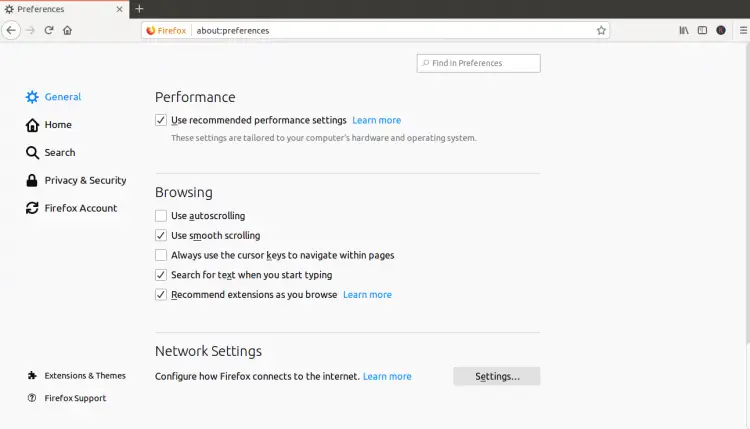
Go to the client system, open the Mozilla web browser, and click on the Edit => Preferences as shown below:
Click on the Network Settings section and click on the Settings. You should see the following page:
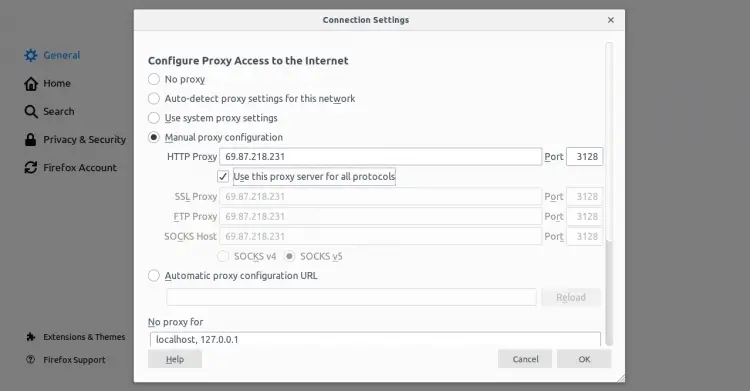
Select the Manual proxy configuration radio button, enter your Squid server IP address in the HTTP Host field and 3128 in the Port field and select the Use this proxy server for all protocols check box and click on the OK button to save the settings.
Now, your browser is configured to browse the Internet through the Squid proxy.
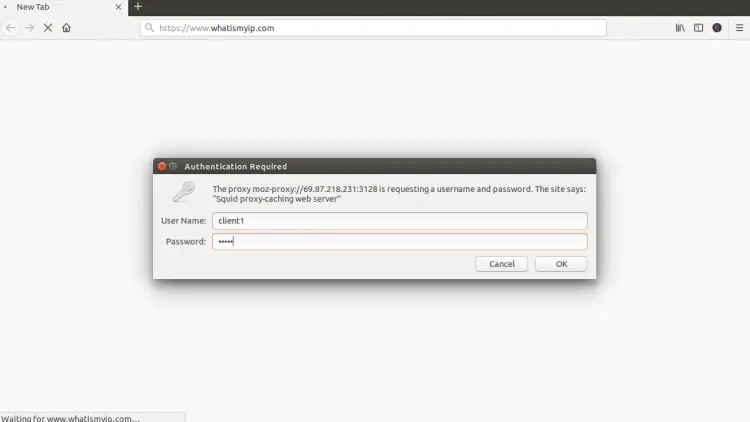
To verify it, type the URL https://www.whatismyip.com/. You will be asked to provide a username and password as shown below:
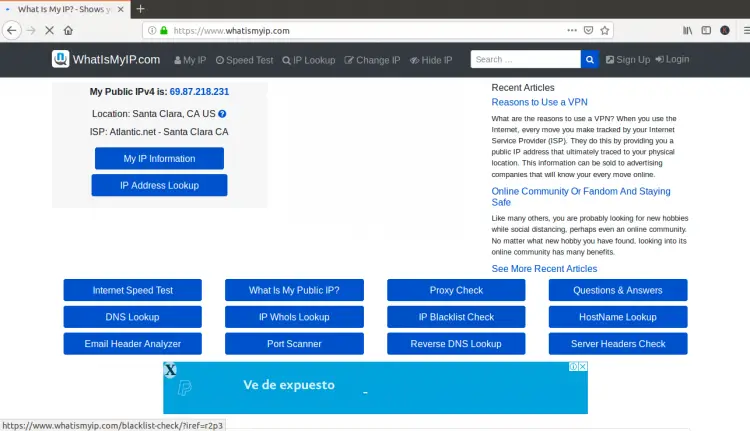
Provide your Squid proxy server username and password which you have created earlier and click on the OK button. You should see the following page:
On the above page, you should see your Squid server’s IP address instead of the IP address of your client computer.
Conclusion
Congratulations! you have successfully installed and configured the Squid proxy server on Ubuntu 20.04 server. You can also configure Squid proxy to restrict the specific website based on the word, domain and IPs. For more information, visit the Squid official documentation.
Đăng ký liền tay Nhận Ngay Bài Mới
Subscribe ngay
Cám ơn bạn đã đăng ký !
Lỗi đăng ký !








Add Comment