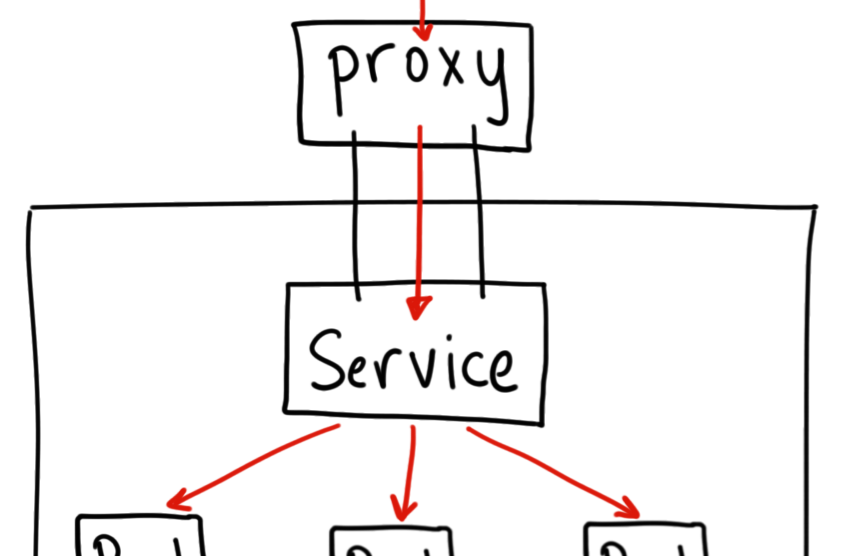
A service is an abstraction layer over Pods. It defines a logical set of Pods. It provides a single IP address and DNS name by which pods can be accessed. It is used to expose the pods.
There are 3 different types of Services in Kubernetes:
- ClusterIP:
It exposes the service within the Kubernetes cluster. This Service is only reachable from within the cluster. It can not be accessed from outside the cluster. - NodePort:
It will expose the service on a static port on the deployed node. This service can be accessed from outside the cluster using the NodeIP:Nodeport. - Load Balancer:
Exposes the Service externally using a cloud provider’s load balancer, this creates a Public IP on the Cloud provider - ExternalName:
It maps the Service to the contents of the externalName field by returning a CNAME record
Click here to know more about Kubernetes Service.
In this article, we will see the steps to create a Serice of type NodePort.
Pre-requisites
- Kubernetes Cluster with at least 1 worker node.
If you want to learn to create a Kubernetes Cluster, click here. This guide will help you create a Kubernetes cluster with 1 Master and 2 Nodes on AWS Ubuntu 18l04 EC2 Instances.
What we will do
- Create a Service
Create a Service
First, we will create a deployment using the following definition to which the service will redirect all requests coming to it.
Create a new file and add the following content in it, this will create a deployment for Nginx.
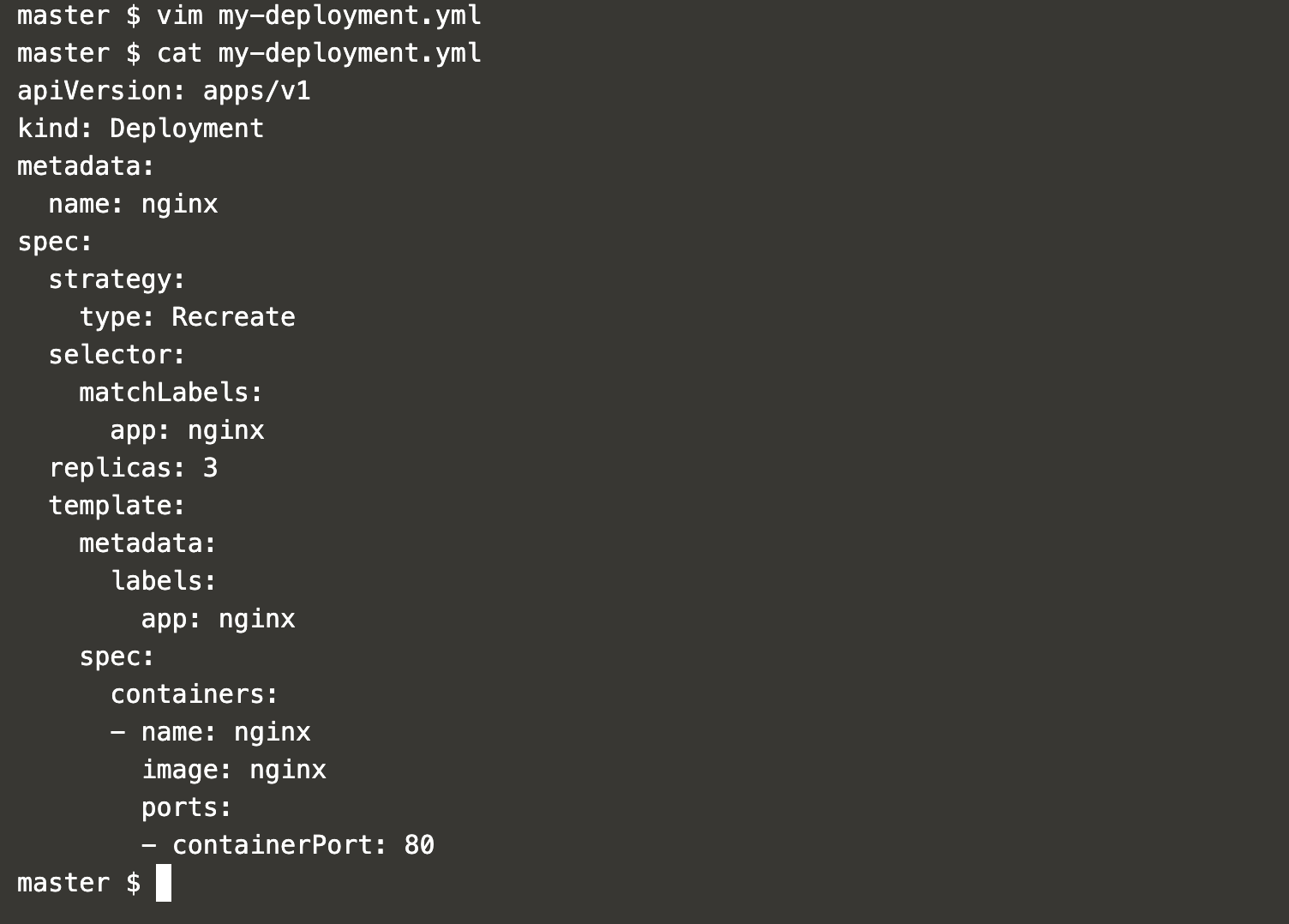
vim my-deployment.ymlapiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
strategy:
type: Recreate
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 3
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
To create a deployment, execute the following command.
kubectl create -f my-deployment.yml
This will create a deployment for Nginx with 3 replicas.
You can get the details of deployment, replicaset and pod using the following commands.
kubectl get deployment | grep nginxkubectl get replicaset | grep nginxkubectl get pod | grep nginx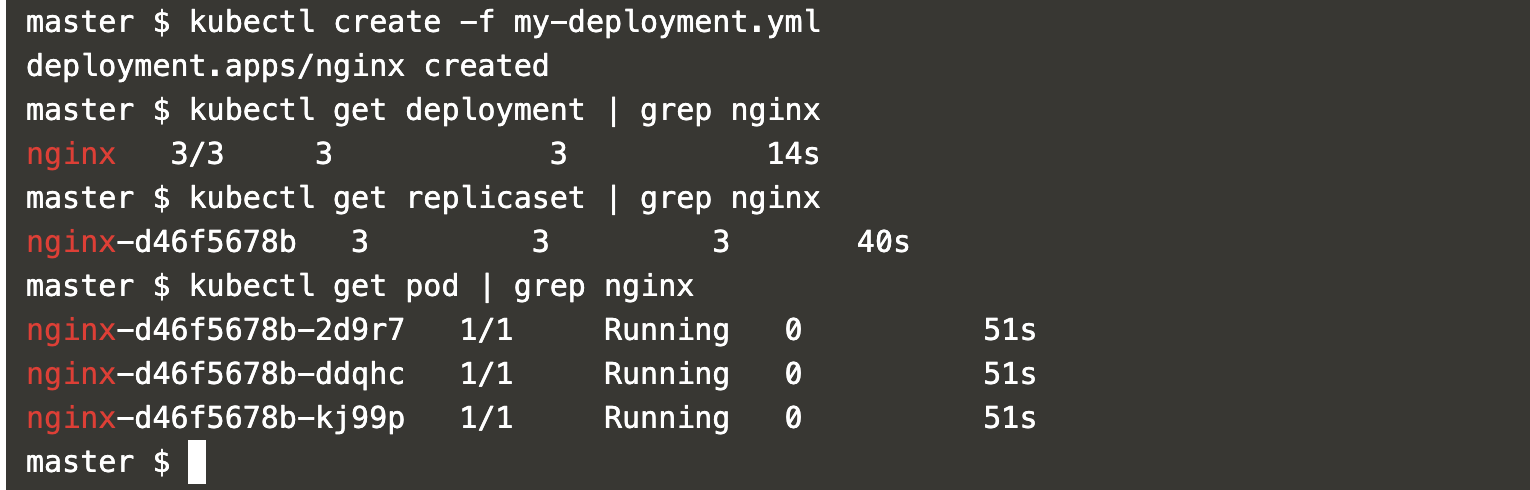
In the above screenshot, you can see 3 replicas of the Nginx have been created.
Now, create a Service definition using the following content.
vim my-service.ymlapiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: default
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
externalTrafficPolicy: Local
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: nginx
type: NodePort
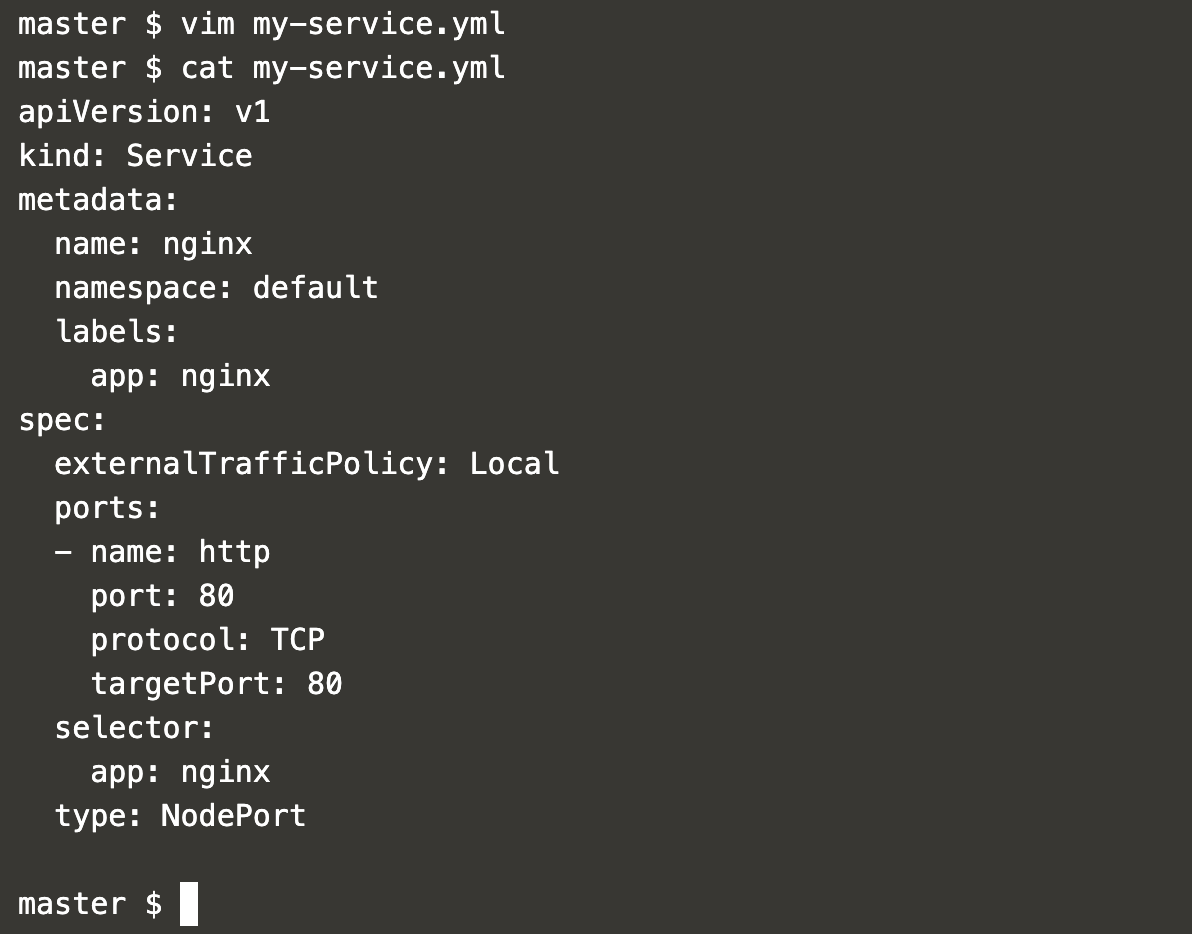
The above service definition will create a Service of type NodePort and redirect requests to Pod matching label nginx, i.e. pods we created using the previous deployment creation step.
Execute the following command to create a Service.
kubectl create -f my-service.yml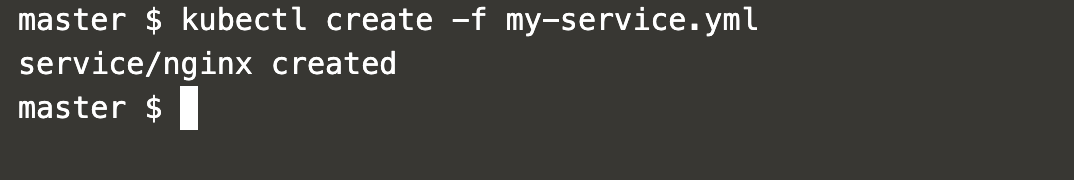
Get the details of the service and check for the NodePort on which the service will be available.
kubectl get service | grep nginxkubectl describe service nginx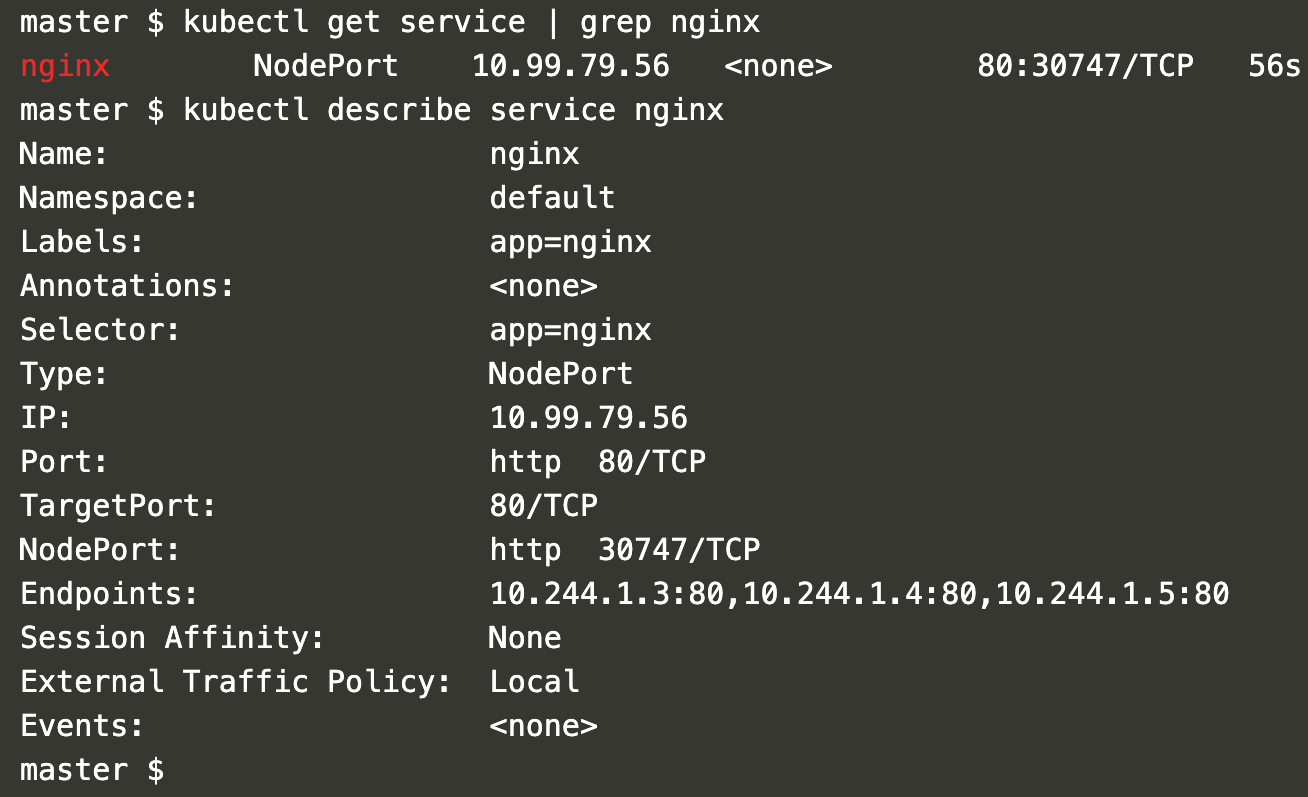
In the above screenshot, it can be seen that the Service is available on Port 30747. This can be different for you as the port is randomly assigned from the available range.
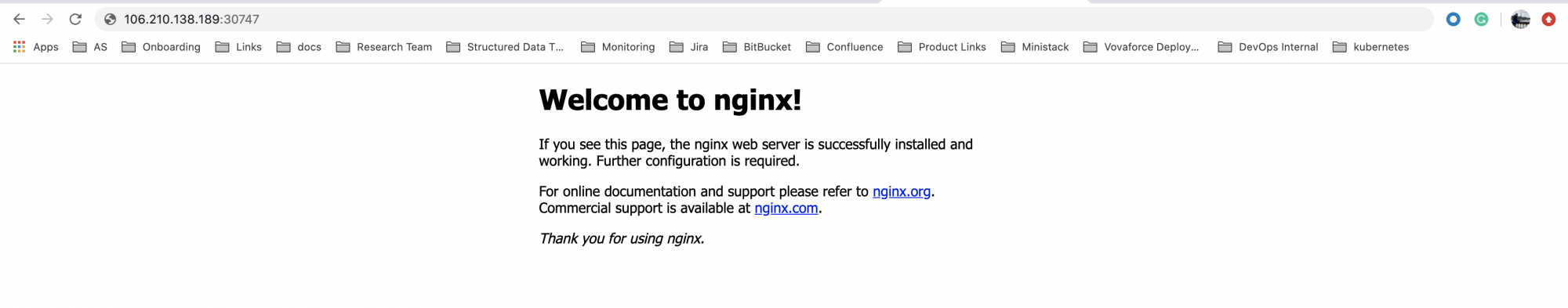
Now, the nginx application can be accessed through this service on NodeIp:NodePort
Here, it is: 106.210.138.189:30747
Conclusion
In this article, we created a deployment for Nginx with 3 replicas and created a Service of type NodePort. We saw how the Nginx application created using the deployment can be accessed on NodeIP:Port.
Nhấn Subcribe để nhận thêm nhiều bài viết mới Like Facebook
[maxbutton id=”2″ ] [maxbutton id=”3″ ]
Đăng ký liền tay Nhận Ngay Bài Mới
Subscribe ngay
Cám ơn bạn đã đăng ký !
Lỗi đăng ký !

![[Cập nhật] Lỗ hổng zero-day 10 điểm trong hệ điều hành tường lửa PAN-OS](https://congdonglinux.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/image_404-scaled.jpg)







Add Comment