How to Install OpenMRS on Ubuntu 22.04
OpenMRS is an efficient electronic medical record (EMR) storage and retrieval system released as open-source software. It helps deliver health care in developing countries to treat millions of HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis (TB) patients. It is founded on the principles of openness to exchange patient data with other medical information systems. You can manage all electronic medical records via OpenMRS web-based interface.
This tutorial will explain how to install OpenMRS software on Ubuntu 22.04.
Prerequisites
- A server running Ubuntu 22.04.
- A root password is configured on the server.
Install OpenJDK 8
OpenMRS is a Java-based application and only supports Java version 8. So you will need to install Java 8 to your server. You can install it using the following command.
apt install openjdk-8-jdk
Next, verify the Java version using the following command:
java -version
You will get the following output:
openjdk version "1.8.0_352"
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_352-8u352-ga-1~22.04-b08)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.352-b08, mixed mode)
At this point, Java 8 is installed on your server. You can now proceed to install the MySQL server.
Install MySQL Server 5.6
Now, you will need to install MySQL server version 5.6 on your server. Because OpenMRS only supports MySQL version 5.6. By default, MySQL 5.6 is not available in the Ubuntu 22.04 default repository. So you will need to install it from the source.
First, create a user and group for MySQL using the following command:
groupadd mysql
useradd -g mysql mysql
Next, download MySQL 5.6 source from their official website using the following command:
wget https://dev.mysql.com/get/Downloads/MySQL-5.6/mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
Next, extract the downloaded file with the following command:
tar -xvf mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
Next, move the extracted directory to /usr/local with the following command:
mv mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 /usr/local/mysql
Next, change the directory to the /usr/local/mysql directory and set proper ownership with the following command:
cd /usr/local/mysql
chown -R mysql:mysql *
Next, install the required dependencies using the following command:
apt-get install libaio1 libncurses5 libnuma-dev -y
Next, run the following script to install MySQL server:
scripts/mysql_install_db --user=mysql
You will get the following output:
You can start the MySQL daemon with:
cd . ; ./bin/mysqld_safe &
You can test the MySQL daemon with mysql-test-run.pl
cd mysql-test ; perl mysql-test-run.pl
Please report any problems at http://bugs.mysql.com/
The latest information about MySQL is available on the web at
http://www.mysql.com
Support MySQL by buying support/licenses at http://shop.mysql.com
New default config file was created as ./my.cnf and
will be used by default by the server when you start it.
You may edit this file to change server settings
Next, set proper ownership to mysql and data directory:
chown -R root .
chown -R mysql data
Next, copy MySQL configuration file and service file to the proper location:
cp support-files/my-default.cnf /etc/my.cnf
cp support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysql.server
Next, start the MySQL service in safe mode:
bin/mysqld_safe --user=mysql &
Next, set the MySQL root password with the following command:
bin/mysqladmin -u root password secure-password
Next, create a symbolic link of the MySQL binary using the following command:
ln -s /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql /usr/local/bin/mysql
Finally, restart your server with the following command:
reboot
After the system restart, start the MySQL service and enable it to start at system reboot:
/etc/init.d/mysql.server start
update-rc.d -f mysql.server defaults
You can now verify the status of the MySQL service with the following command:
/etc/init.d/mysql.server status
You will get the following output:
? mysql.server.service - LSB: start and stop MySQL
Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/mysql.server; generated)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2022-12-13 04:08:18 UTC; 15s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
Tasks: 22 (limit: 2238)
Memory: 455.3M
CPU: 329ms
CGroup: /system.slice/mysql.server.service
??1120 /bin/sh /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld_safe --datadir=/usr/local/mysql/data --pid-file=/usr/local/mysql/data/ubuntu2204.pid
??1228 /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld --basedir=/usr/local/mysql --datadir=/usr/local/mysql/data --plugin-dir=/usr/local/mysql/lib/…
Dec 13 04:08:17 ubuntu2204 systemd[1]: Starting LSB: start and stop MySQL...
Dec 13 04:08:17 ubuntu2204 mysql.server[1112]: Starting MySQL
Dec 13 04:08:18 ubuntu2204 mysql.server[1112]: . *
Dec 13 04:08:18 ubuntu2204 systemd[1]: Started LSB: start and stop MySQL.
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Install Tomcat 8
Next, you will need to install Tomcat 8 to deploy OpenMRS.
First, create a user and group for Tomcat with the following command:
groupadd tomcat
useradd -s /bin/false -g tomcat -d /opt/tomcat tomcat
Next, download the Tomcat 8 from their official website using the following command:
wget https://dlcdn.apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-8/v8.5.84/bin/apache-tomcat-8.5.84.tar.gz
Next, create a directory for Tomcat and extract the downloaded file to /opt/tomcat directory:
mkdir /opt/tomcat
tar -xvzf apache-tomcat-8.5.84.tar.gz -C /opt/tomcat/ --strip-components=1
Next, set proper ownership to /opt/tomcat directory:
chown -R tomcat:tomcat /opt/tomcat
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Create a Systemd Service File for Tomcat
Next, you will need to create a systemd service file to manage the Tomcat service. You can create it with the following command:
nano /etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service
Add the following lines:
[Unit]
Description=Apache Tomcat Web Application Container
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
Environment=JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-amd64
Environment=CATALINA_PID=/opt/tomcat/temp/tomcat.pid
Environment=CATALINA_HOME=/opt/tomcat
Environment=CATALINA_BASE=/opt/tomcat
Environment=’CATALINA_OPTS=-Xms512M -Xmx1024M -server -XX:+UseParallelGC’
ExecStart=/opt/tomcat/bin/startup.sh
ExecStop=/opt/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh
User=tomcat
Group=tomcat
UMask=0007
RestartSec=10
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and close the file then reload the systemd daemon to apply the changes:
systemctl daemon-reload
Next, start the Tomcat service with the following command:
systemctl start tomcat
You can now verify the status of the Tomcat service with the following command:
systemctl status tomcat
You will get the following output:
? tomcat.service - Apache Tomcat Web Application Container
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2022-12-13 04:11:30 UTC; 7s ago
Process: 1394 ExecStart=/opt/tomcat/bin/startup.sh (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 1401 (java)
Tasks: 28 (limit: 2238)
Memory: 97.0M
CPU: 2.192s
CGroup: /system.slice/tomcat.service
??1401 /usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-amd64//bin/java -Djava.util.logging.config.file=/opt/tomcat/conf/logging.properties -Djav>
Dec 13 04:11:30 ubuntu2204 systemd[1]: Starting Apache Tomcat Web Application Container...
Dec 13 04:11:30 ubuntu2204 startup.sh[1394]: Tomcat started.
Dec 13 04:11:30 ubuntu2204 systemd[1]: Started Apache Tomcat Web Application Container.
At this point, Tomcat is started and listens on port 8080. You can now proceed to the next step.
Install OpenMRS Ubuntu 22.04
First, create a directory for OpenMRS and set proper ownership with the following command:
mkdir /var/lib/OpenMRS
chown -R tomcat:tomcat /var/lib/OpenMRS
Next, download the latest version of OpenMRS using the following command:
wget https://sourceforge.net/projects/openmrs/files/releases/OpenMRS_Platform_2.5.7/openmrs.war
Once the download is completed, copy the downloaded file to the Tomcat webapps directory:
cp openmrs.war /opt/tomcat/webapps/
Next, change the ownership of the openmrs.war file to tomcat:
chown -R tomcat:tomcat /opt/tomcat/webapps/openmrs.war
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Perform OpenMRS Installation via Web Browser
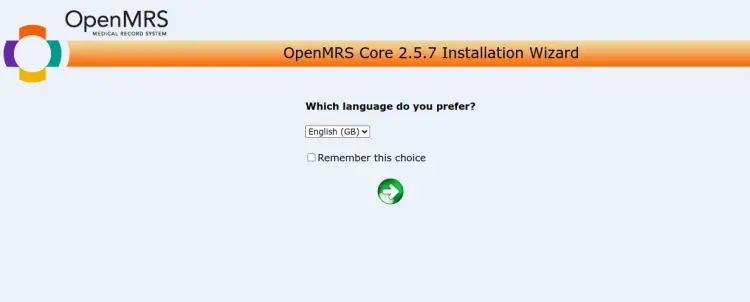
Now, open your web browser and access the OpenMRS web installation wizard using the URL http://your-server-ip:8080/openmrs. You should see the OpenMRS language selection screen:
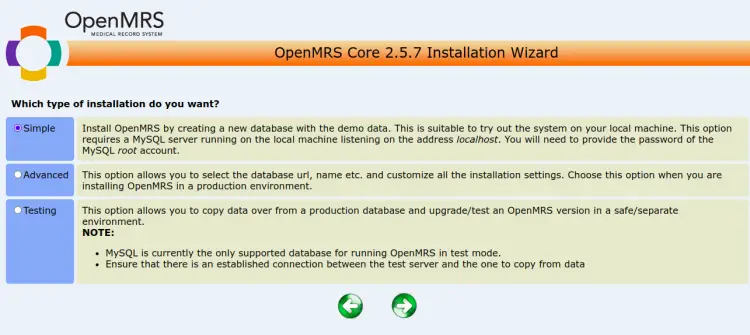
Select your language and click on the => button. You should see the Installation Type screen.
Select the type of installation you want and click on the => button. You should see the following screen:
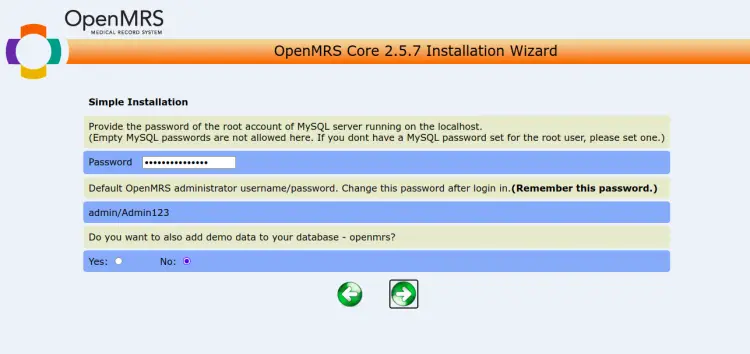
Provide your MySQL root password, note down the admin password, and click on the => button. You should see the following screen:
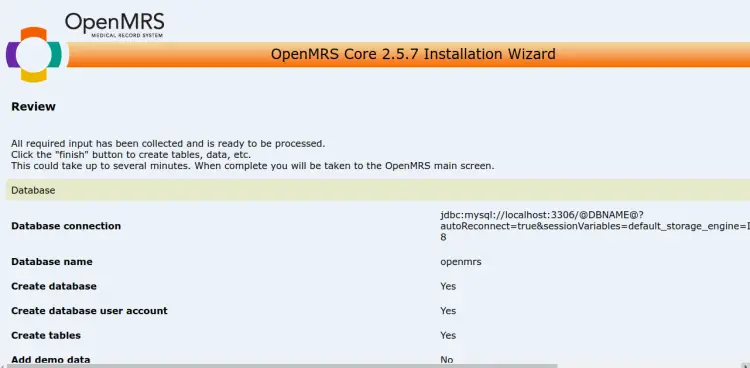
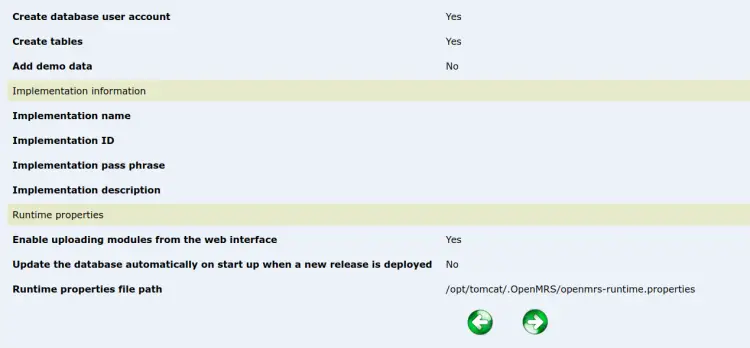
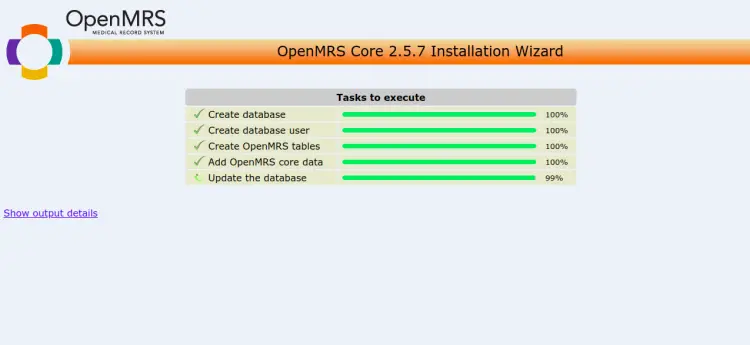
Click on the => button to create a database for OpenMRS and complete the installation.
Provide the default username as admin and password as Admin123, then click on the LOG IN button. You should see the OpenMRS dashboard on the following screen:
Conclusion
Congratulations! you have successfully installed OpenMRS on Ubuntu 22.04. I hope this post will help you to deploy OpenMRS on Linux based system to store and manage the electronic medical record. For more information, visit the OpenMRS documentation page. Feel free to ask me if you have any questions.
Đăng ký liền tay Nhận Ngay Bài Mới
Subscribe ngay
Cám ơn bạn đã đăng ký !
Lỗi đăng ký !











Add Comment