Introduction
Pip (Pip Installs Packages) is a software utility that downloads and manages packages from PyPI – the Python Package Index.
Pip is a command-line program; when installed, it adds the pip command line to the system. Use the tool to install and manage Python software packages.
In this article, learn how to install pip on Ubuntu.
Prerequisites
- A Ubuntu system.
- Access to a user account with sudo privileges.
- Access to a terminal window/command line (Ctrl+Alt+T).
Note: If you are using Python in a virtual environment created with pyvenv or virtualenv, then pip is available regardless of the version of Python in use. This also applies to Python 2.7.9 or newer (Python series 2) and Python 3.4 or later (Python series 3).
Install Pip for Python 3
Ubuntu comes with Python 3 installed by default, but it does not come with pip. To install pip for Python 3 on Ubuntu:
1. Open the terminal. The simplest way is to right-click the desktop and select Open Terminal from the drop-down menu.
2. Update the repository package list by running the following command in the terminal:
sudo apt update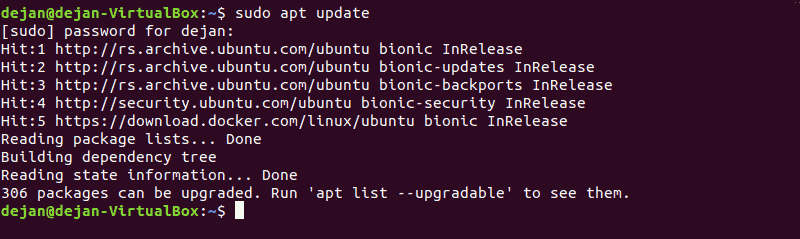
3. Install pip for Python 3 and all the dependencies for building Python modules by running the following command:
sudo apt install python3-pip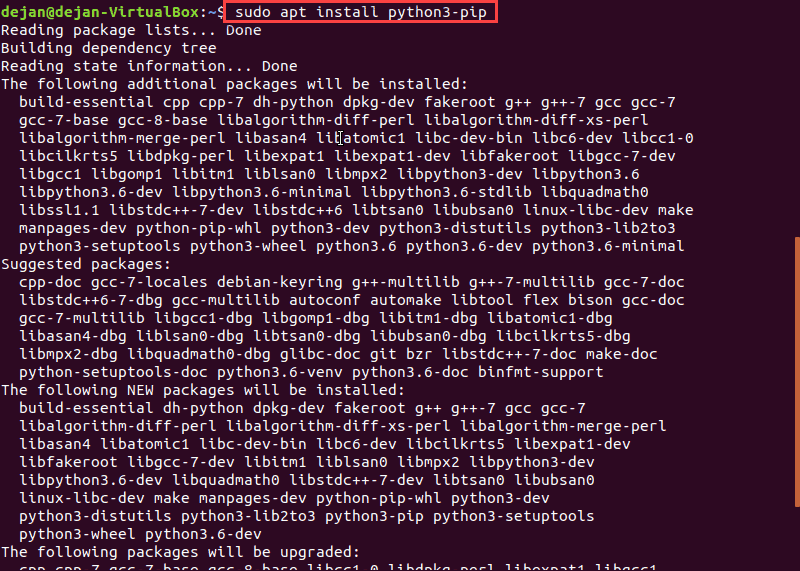
When prompted, type Y and hit Enter to confirm the install.
4. To verify the install run the following command:
pip3 --versionThe installed version might be different in your case, but the general output should resemble the line below:

5. To upgrade pip3 to the latest version, issue the --upgrade command just like for any other PyPI package:
sudo pip3 install --upgrade pip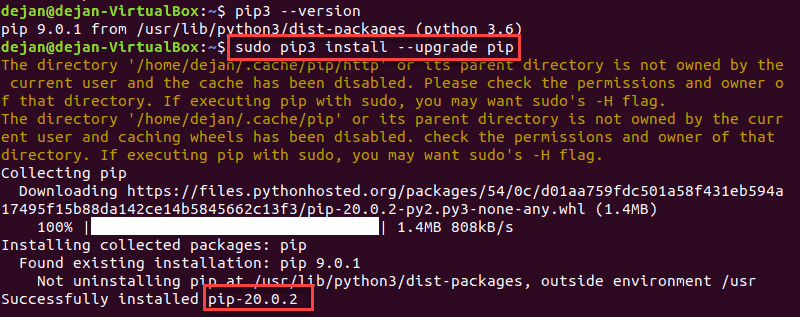
Install Pip for Python 2
To install pip for Python 2 on Ubuntu:
1. Open the terminal using the CTRL+ALT+T shortcut.
2. Update the repository package list by running the following command:
sudo apt update3. Install pip2 for Python 2 and all the dependencies for building Python modules by running:
sudo apt install python-pip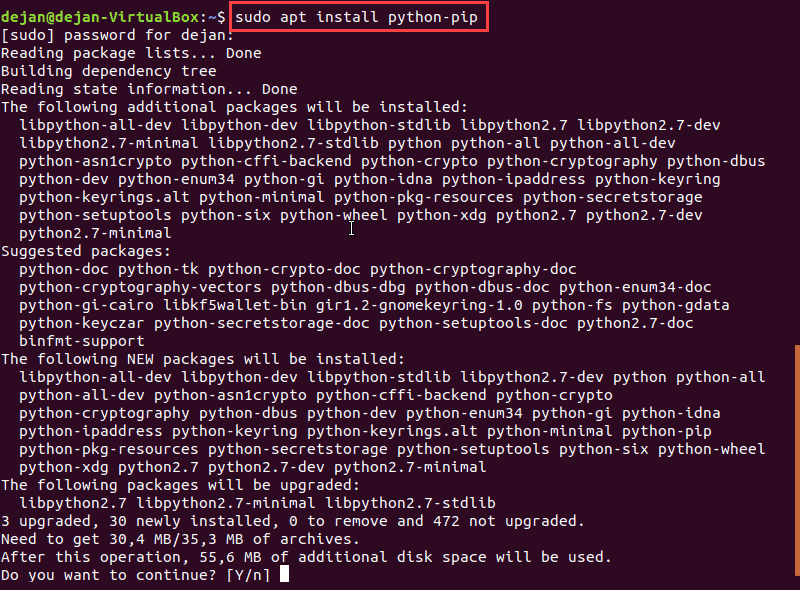
If prompted, type Y and hit Enter to complete the installation.
4. To verify the install run the following command:
pip2 –-versionAt the time of writing this article, the latest version of Pip is 9.0.1, but this may vary.
OUTPUT
pip 9.0.1 from /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (python 2.7)5. To upgrade pip for Python 2 to the latest version, run the --upgrade command:
sudo pip2 install --upgrade pipEssential Pip Commands
The sections below cover the most essential Pip commands.
Note: If you are using Pip for Python 3 on Ubuntu 22.04, use pip instead of pip3 in the commands. If using Python 2, some commands will not work correctly due to deprecation.
List All pip Packages
To list installed Pip packages, use the following command:
pip3 listSearch For a Package
Search for a particular package by running:
pip3 search enter_search_termInstalling Software Packages
Type the following command to install the latest version of a software package:
pip3 install Enter_Package_NameTo install a specific version of a software package, specify the version after the software package name.
For example:
pip3 install Enter_Package_Name==2.4Uninstalling a Package
To remove a Python package, type:
pip3 uninstall Enter_Package_Name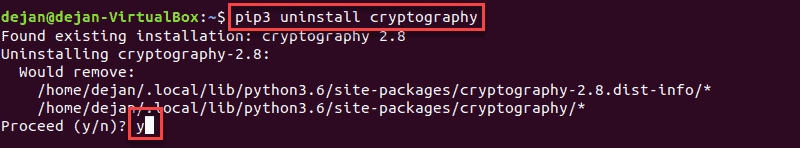
When prompted, type Y and hit Enter to confirm.
Getting a List of Outdated Packages
To prompt a list of installed outdated packages and see the latest versions available, enter:
pip3 list --outdatedSee below for a sample output:
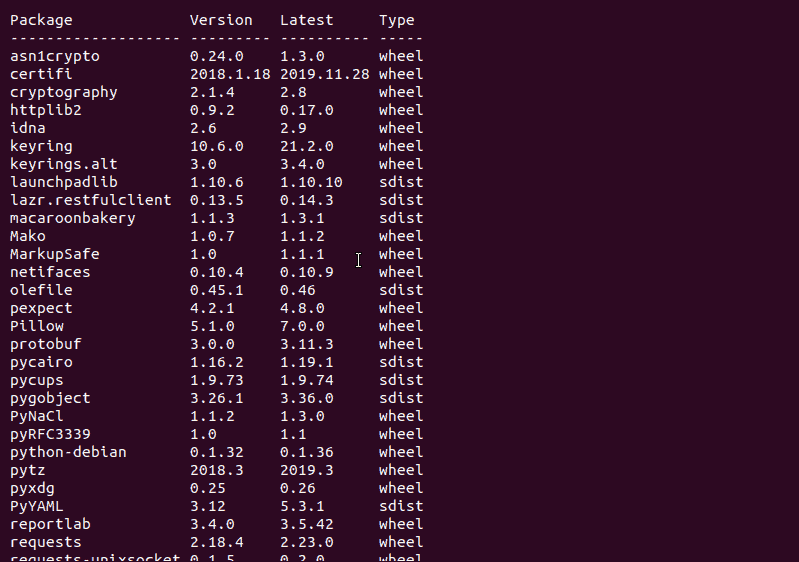
Pip Update Packages
Similar to the apt upgrade command, Pip can also be used to upgrade a software package to the latest version:
pip3 install --upgrade Enter_Package_Name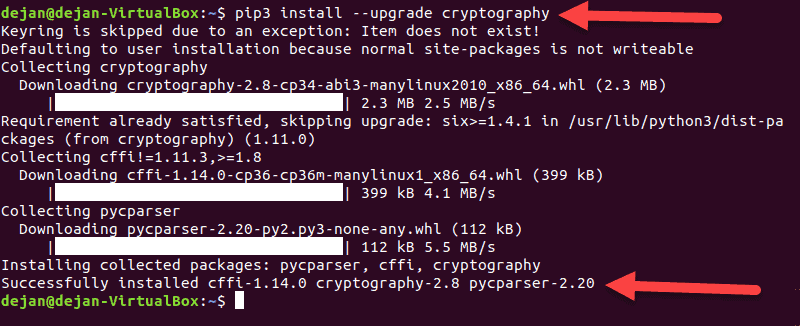
Get Additional Details
To prompt additional details, run the following command:
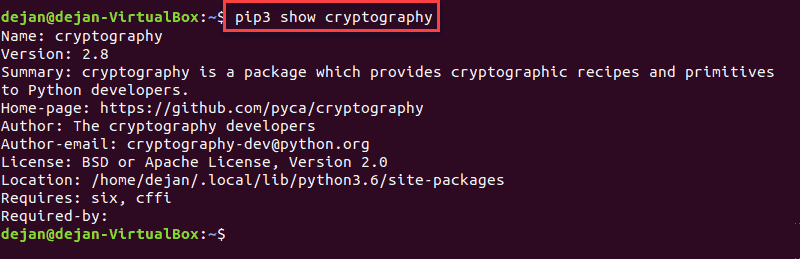
pip3 show Enter_Package_NameSee a sample output below:
Setup Python Virtual Environments (Optional)
To create a virtual environment, the python-venv module is required.
Install the module with the following terminal command:
sudo apt install python3–venvWe are using the apt package installer because we’re installing the python-venv module globally.
Once that process completes, you can create a virtual environment for Python. Change the directory to a location where you want to store your virtual environment. For example:
/users/username/pythonEnter the following command to create a virtual environment in that path:
python3 –m venv my_test_environmentReplace my_test_environment with the name of your project. This environment includes Python, Pip, the Python library, and supporting files. A new directory will be created with the name you provide.
Activate the virtual environment with the following command:
source my_test_environment/activateThe command line changes to indicate that you are operating within the new Python virtual environment. From here, you can use Pip to install a module only to this environment.
For instance:
pip install module_nameConclusion
With this guide, you have learned how to install Pip on Ubuntu for Python 2 and Python 3.
Keep in mind that Pip is used specifically for Python packages in the Python Package Index (PyPI).
NumPy is a library for the Python programming language, adding support for large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices. Check out our guide and learn how to install NumPy using PIP.
Đăng ký liền tay Nhận Ngay Bài Mới
Subscribe ngay
Cám ơn bạn đã đăng ký !
Lỗi đăng ký !




Add Comment